Home >> Blog >> What is Blockchain Technology and Everything You Need to Know About It
What is Blockchain Technology and Everything You Need to Know About It
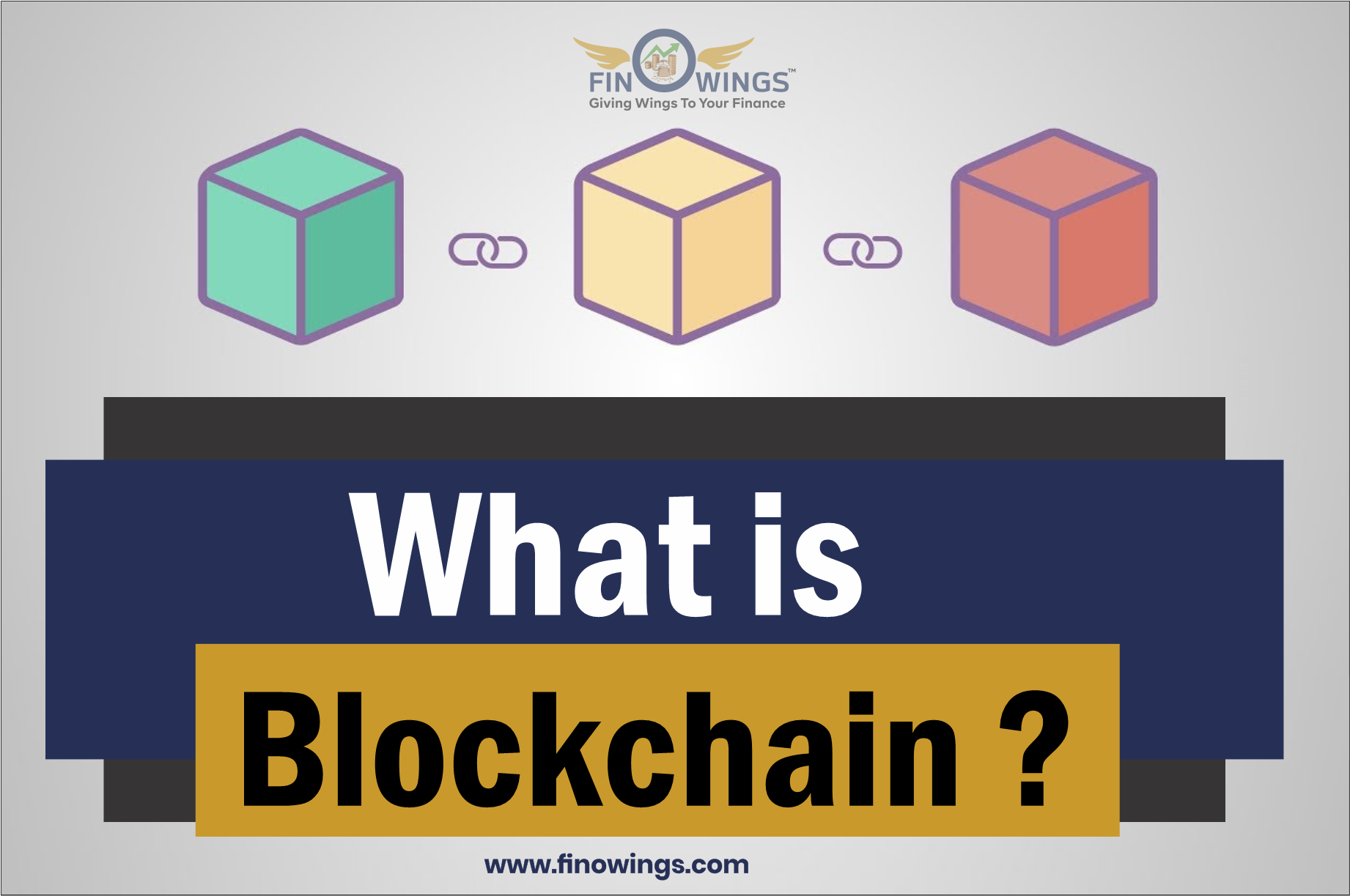
Table of Contents
One of the most widely used technologies in the current digital era is blockchain. Blockchain technology is being used in a number of industries, including supply chains, banking, cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin and even healthcare where it is drastically changing how people exchange information and move money.
The majority of the world is still unfamiliar with blockchain technology and many people are still confused about what it is and how it may be used. In this blog, we provide the most basic explanation of what and how it works, why it is secure and what makes it revolutionary by using simple real-world examples and step-by-step explanations throughout the guide on blockchain for beginners.
What Is Blockchain?
What is Blockchain? A good starting point is a simple understanding of what a ledger is. A ledger is like a record book that particularly stores information permanently and transparently.
Incorporating the Simple Definition
Blockchain is a technology that records data in blocks and chains them together. Unlike a central server, the blocks are stored in a distributed manner, where the recipients are part of the network. As such, the key points of information are:
- Data is stored in blocks.
- Blocks are linked and protected with cryptography.
- Data is dispersed across a network of computers.
- Once input, data does not change easily.
It is for all these reasons that the explanation of blockchain includes the explanation of immutable which is a descriptive term for (digital) ledger.
Why Is Blockchain Necessary?
Conventional systems have some key issues:
- A single central authority controls everything.
- Information can be changed or hacked.
- There is a lack of transparency.
- Trust in the system depends on middlemen.
Blockchain technology eliminates all these issues by creating a trustless system where verification is done automatically through code and consensus.
How Blockchain Works: Blockchain Explained
Let’s break down how blockchain works in the simplest way possible.
Step 1: A Transaction is Created
A user starts a transaction. An example transaction could involve:
- Sending money to someone.
- Recording a new owner of an asset.
- Sharing private data with someone.
- The transaction is sent to the blockchain network.
Step 2: Transaction Gets Verified
The transaction gets verified through many computers called nodes.
Each of them asks:
- Is the sender a valid user of the network?
- Does the sender have a sufficient balance to make the transaction?
- Is the transaction valid given the network’s rules?
There is no single authority that is in control of this process.
Step 3: Transaction is Added to a Block
When the transactions are verified by the network, the transactions:
Join a group of transactions that are verified.
-
Form a block on the blockchain.
Each block on the blockchain includes:
- The data of all the transactions in the block.
- The date and time the block was created.
A unique cryptographic code that identifies the block (this is called the block's hash). The hash from the last block on the blockchain.
Step 4: Block is Added to the Blockchain
The new block is added to the most recent block in the blockchain using cryptographic links. This makes a chain of blocks; this is why it's called a blockchain. If someone tries to change any data in the block, the following will happen:
- The hash of the block will change.
- The chain of blocks will break (this is how the network knows a block was tampered with).
- The network will immediately reject the tampered block.
Step 5: Blockchain is Updated Across the Network
The updated blockchain is:
- Distributed on all of the nodes in the network.
- Maintained in a large number of locations.
This is how the blockchain becomes:
- Decentralised (no single point of failure).
- Transparent (anyone can see the data).
- Highly secure (no single point of attack).
- This is the basis of how blockchain works.
What Makes Blockchain Secure?
The security of the data is one of the biggest benefits of blockchain technology.
1. Decentralisation
-
There is no single point of control over the data.
-
If one computer shuts off, the whole network keeps running.
2. Cryptography
-
Each block is created using complex encryption (this is called hashing).
-
Because of this, altering any of the data in the block is almost impossible.
3. Consensus Method
Before new information is added, all participants in the network must validate what is being added. Some of the most common consensus methods include:
-
Proof of Work (PoW).
-
Proof of Stake (PoS).
4. Immutability
If data is entered, it cannot be altered except by modifying the entire chain.
Blockchain Using A Sample
Picture a Google Sheet that:
- It is jointly owned by thousands of individuals.
- Everyone can view it and see updates.
- No one can overtly modify the previous data.
- All edits are recorded in an audit log.
This is a blockchain because of the shared, tamper-proof Google Sheet.
Kinds Of Blockchain
Beginners must recognise the types of blockchain.
1. Public Blockchain
Anyone can use it.
- Anyone can get involved.
- Totally decentralised.
Example use cases:
- Digital currencies
- Public networks
2. Private Blockchain
- Managed by one company solely.
- Limited access.
- Quick transactions.
Used by:
- Financial institutions.
- Companies.
3. Consortium Blockchain
- Managed by a collection of companies.
- Partially decentralised.
Used in:
- Logistics.
- Cross-border banking.
Blockchain Technology: Key Features
These are the main features that define blockchain technology:
- No single central authority.
- Transparent transactions.
- Highly secured.
- Trust without middlemen.
- Unalterable records.
These features make blockchain perfect for sensitive information and financial systems.
Common Use Cases
Blockchain isn’t only for crypto.
Popular Blockchain Use Cases
- Online transactions
- Automated contracts
- Logistics management
- Digital ID
- Medical records
- Election systems
This rapid uptake is indicative of a technology that is ready for the future.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
Key Benefits
- Removes intermediaries.
- Lowers costs.
- More transparency.
- Better security.
- Quicker transactions.
These benefits explain why blockchain technology is being adopted globally.
Limitations of Blockchain
Blockchain has many advantages, but there are also challenges that come with it.
Common Limitations
- Dealing with scalability.
- High energy use (some networks).
- Unclear regulations.
- Great technical difficulty.
Both advantages and drawbacks are important to know when drafting any blockchain guide.
Blockchain vs Traditional Systems
|
Feature |
Blockchain |
Traditional System |
|
Control |
Decentralized |
Centralized |
|
Transparency |
High |
Limited |
|
Security |
Very high |
Moderate |
|
Data alteration |
Nearly impossible |
Possible |
|
Trust |
Code-based |
Authority-based |
Is Blockchain the Future?
Most experts agree that blockchain will:
- Power the next generation of finance.
- Secure digital identities.
- Enhance global transparency.
However, like the internet in its early days, the evolution will happen gradually.
Blockchain Guide for Beginners: Key Takeaways
If you're new to blockchain, keep in mind:
- Blockchain is a technology just cryptocurrency.
- It builds trust through math and code, not relationships.
- It eliminates the need for intermediaries.
- Starting with the basics is the most logical approach.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a decentralised system that records data securely and transparently. Thinking about how blockchain works shows newbies why it's trusted with no central control. As adoption increases, blockchain will be foundational to the future of finance, information and digital systems.
DISCLAIMER: This blog is NOT any buy or sell recommendation. No investment or trading advice is given. The content is purely for educational and information purposes only. Always consult your eligible financial advisor for investment-related decisions.
Author
Frequently Asked Questions
Absolutely yes, a company can put up a private blockchain to keep its sensitive data.
The price to set up a private blockchain varies depending on the company. The criteria, blockchain platforms, technologies, and tools a company utilises are some of the factors that affect how much a blockchain project will cost.
Blockchain technology is reliable, and the codes it uses are incorporated into the digital code. This technique distributes the data it stores among a number of nodes. One must break each node in order to hack this system. Although arduous, the work is not insurmountable. Thus, we can draw the conclusion that while blockchain technology is secure, it is not completely immune to hacking.
Some of the fundamental characteristics of blockchain include decentralisation, improved security, distributed ledgers, and consensus algorithms.
Blockchain technology uses a lot of electricity, which can lead to pollution that is bad for the environment and can cause greenhouse gas emissions.





















